Body Fat: The Definitive Guide (Part 1)
I suppose we all want good looks, fitness and health, right?
Well everyone wants to have a great body. It’s because among the best indicators of both health and beauty is your body fat. Excessive body fat, especially in obesity levels is associated with serious health risks and also very few sexual partners. Now although it’s not everyone’s goal to have the erotic life of Casanova, having options is a must. Still health is considered the major problem when it comes to body fat.
Did you know that obesity levels keep rising around the globe?
According to WOF (World Obesity Federation), obesity rate was 11,5% for 2010 and it rose to 13% for 2014. It is expected that by 2025, it will rise to 17%. Therefore it concerns us all to be well educated around the physiology of our body and what risks may be involved in extra body fat.
But let’s start with a very fundamental question.
What exactly is body fat?
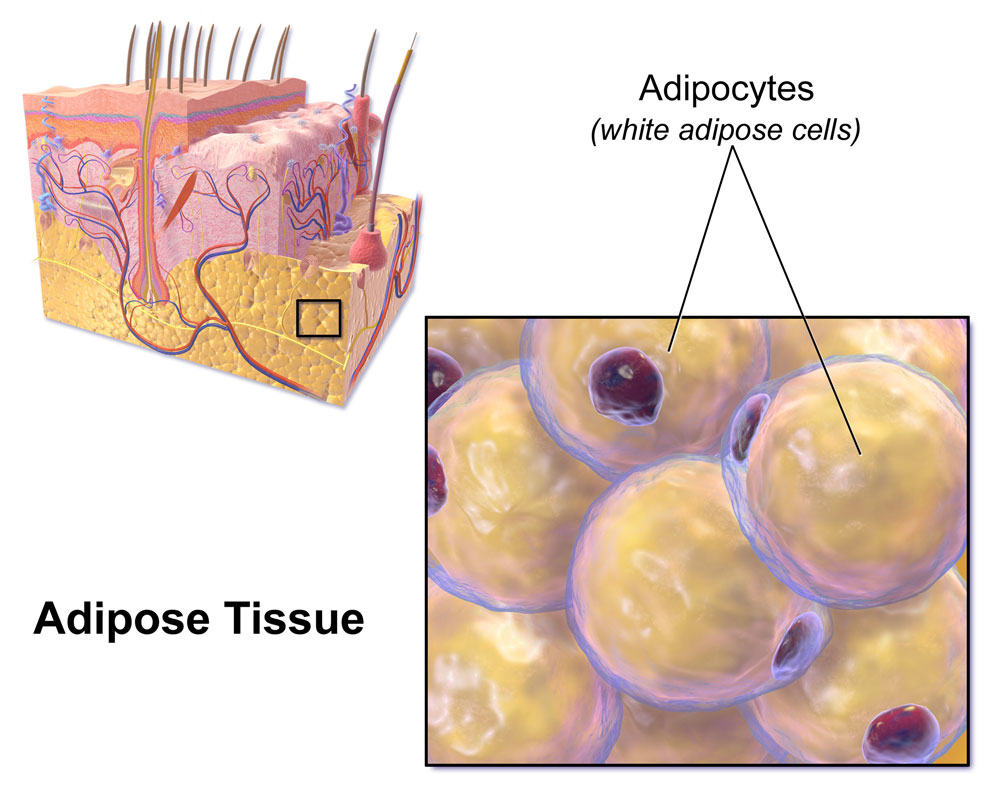
Biology wise, body fat or “Adipose tissue” is loose connective tissue composed of adipocytes (fat cells). Its primary role is to store energy in the form of lipids but also to protect and insulate the body. Besides that, fat is considered a large endocrine organ, since it produces hormones like leptin, estrogen, resistin and cytokines.
There are two very broad categories of fat which are, White Adipose Tissue and Brown Adipose Tissue. White is used as energy storage, while brown is used mainly for generating heat. As humans, we have a lesser amount of brown fat compared to other mammals, but still we have some. Infants have an even greater amount, 5% of their total mass is attributed to brown fat tissue.
Another cool thing is that the density of fat is approximately 0.9g per ml, while muscular tissue is around 1.06g per ml. This means that a “fatter” person is able to float on the water more easily than a more muscular one.
Obviously fat is created and maintained by the body because it is beneficial. Some of these benefits are:
- Fat soluble vitamins like A, D ,E and K, are absorbed through fat globules
- Prolonged energy levels. Fat is our biggest source of stored energy
- Immune system functionality
- It promotes testosterone levels
From an evolutionary perspective, we need to have fat storages in case of a fasting period due to lack of food supplies. But this thing has changed in our present environment. We have next to zero reasons, to have extra body fat since we are always in a surplus of food supplies. This came along with agriculture and animal farming. Agriculture has been around for 11,500 years. Although it may sound like a long time, evolutionarily is only a small fragment of time. The point is that we haven’t created yet sophisticated preventive mechanisms for obesity such as for lack of food. It is true that leptin is a hormone that regulates our appetite but it doesn’t protect us that much from binging. Hunger is such a preventive mechanism, that is actually irritating and worsens our mood, in order to incentive us go look for supplies. Thus, we are confronted with another problem which is obesity, or excessive body fat.
A first approach to calculate body fat for health reasons was the body mass index
Body Mass index (BMI)
BMI was devised by Adolphe Quetelet from 1830 to 1850, as Quetelet index. It got its present name, from a paper published in July of 1972 by Ancel Keys. BMI calculates the relationship of your weight compared to your height and the value of the result is compared to an index of ranges, in order to assess if you are underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
Although this index may prove useful, it is better used in population studies. Individuals can be totally misled with BMI. The classic example is a very lean, muscular fellow.
Eg. a 180 lbs (81,5kg) person, with height 5’ 11’’ (1.80m) is considered borderline overweight.
This person may have 10% body fat and be extra lean. But still this is considered overweight according to BMI. Therefore, it is a useless index for an athlete or someone who exercises regularly. It is far more valuable to know your body fat percentage rather than your BMI.
So body fat is rather a problem of quality rather than quantity. A person of 200 lbs or 90 kg may have a greater amount of fat compared to a lighter person but what counts is his body fat percentage. In other words, his body fat tissue compared to everything else in his body.
It’s time to introduce another term, “body composition”.
Body composition
The term is used to describe the percentages of water, bones, muscle and fat, compared to the total weight of the body. Obviously being in a healthy range of body fat and muscle, prevents you from different kinds of health problems, like diabetes, high blood pressure or even some cancers. While being obese is detrimental, being emaciated or abnormally thin could also be fatal. If your body fat is not above a certain percentage (~3%), your body fails to deliver vitamins to the organs, has a non-working reproductive system and your general well-being is compromised.
The two extremes of this condition are presented below


So what is a healthy body fat percentage?
There are ranges according to each lifestyle. For example, an athlete is expected to have a much lower body fat than a sedentary person. Still, the athlete’s body fat is much closer to the ideal, healthy percentage. You didn’t think I was gonna promote sitting on a couch all day, did you?
The general guideline for healthy body fat is around 12% for men and 17% for women in the ages of 20-40. After this age is pretty difficult to stay within this percentages but a +5% is perfect.
| Men | Women | |
| Essential | 3% | 10% |
| Athletes | 10% | 15% |
| Fitness | 15% | 22% |
| Average | 18% | 25% |
| Obese | 26%+ | 32%+ |
Body fat is not the only thing in our body as previously mentioned. Everything else in our body is considered lean body mass or LBM.
In essence lean body mass includes:
- organs
- blood
- bone
- muscle
- skin
Organs in case you didn’t know are pretty heavy. Especially the brain (1365-1450 gr) and the liver (1440-1680 gr) are the heaviest ones. Bones are heavy as well, they support the whole muscular system after all. The info you should take away though, is that skeletal muscle is around 42% of body weight for men and 35% for women.
Still, we have to know a little more about body fat. Stay with me.
Types of Body fat
Now the more interesting part is that not all fat is equal. There is another categorisation, regarding the location of body fat. The four general categories are:
- In bone marrow (yellow bone marrow)
- Intramuscular fat (found inside your muscles and between your muscle fibers)
- Visceral fat (found around midsection, specifically surrounding your internal organs)
- Subcutaneous fat (found just below the skin)
Yellow Bone Marrow

Intermuscular fat
You may find it also as intramuscular triglycerides (IMGT) or intermuscular adipose tissue (IMAT). It is the fat found underneath the deep fascia of muscle. More specifically fat between the muscle fibers is called intramuscular fat and between the variant muscle groups is called intermuscular fat, literally.
If you want to have a better idea of the intermuscular fat, try to remember cuts of meat where you see white spots on it and around it, this is the fat around the muscles of the animal.
Visceral Fat
This is the most important and dangerous type of fat. It is stored within the abdominal cavity and mainly around the liver, the pancreas, the heart and the intestines. The body needs a proper amount of fat around these organs but a large amount is very dangerous for your health.
The most apparent indicator of visceral fat is the belly. I am pretty sure you have come across some old people with very large bellies. Sometimes it even seems as stretched out. In this case, it is mostly a combination of both visceral fat and subcutaneous fat. The intra-abdominal fat is our visceral fat.

Subcutaneous Fat
This type of fat is found below the skin (subcutaneous) and it provides insulation from heat and cold. It helps in maintaining our body temperature. Its main function is to store lipids that can be converted to energy to meet the needs of the body. Subcutaneous fat is not related that much to obesity-related pathologies and some evidence even suggests it might be protective. There is a big difference in the places of storing subcutaneous fat for men and women. Typically, the female pattern of fat distribution is below the midsection and specifically around the hips, thighs and glutes. While in men is mostly above the midsection, around the belly and the chest.
This type is also an active part of the endocrine system as it secretes leptin and resistin. Two major hormones.
Our bodies operate in a perfect sense as they take into consideration these types of fat when you are trying to lose weight. The first type to go is also the most dangerous visceral fat. Then the body is trying to use up the subcutaneous fat, which will eventually make us look good in the mirror.
Sometimes a relatively thin person may have a great deal of visceral fat and not so much subcutaneous fat. This could be very tricky because it’s a little difficult to acknowledge it since it’s not visible. This calls for measurement of his/her body fat.
Now we are educated around body fat, its uses, and its benefits. But the main reason we want to know all that is to change our body and have a more fit and muscular look.
Everybody trying to have a better body has to step on the scale.
So what’s the thing with you and the scale?
Get on the scale today
I have read many times that you should look in the mirror instead of getting on the scale. “The mirror is the true indicator”. Although I can’t disagree as a general point, I think there is a fallacy to that.
Most of us are not very competent in measuring the changes in our body just by looking in the mirror. Besides that, there cannot be great changes in your body that are not reflecting the scale in the short term. Most of the time if you look better after a week, you must have lost some weight. This rule, however, has 2 exceptions.
Exception No. 1: Drugs for Performance enhancement
When someone is on drugs or “on a cycle”, they can have extreme changes in their body composition. In other words, they can lose a huge amount of fat, gain muscle and all that while staying at the same weight. By all means, I wouldn’t promote drugs, it is just mentioned for informational reasons. I am strongly against them.
Exception No. 2: Beginners
When you are a beginner, your body is super sensitive to both exercise and dieting. Your body changes with a very fast pace and it tries to compensate for what it does not have. In a very simplistic approach:
- Regarding exercise, it tries to gain muscle because you don’t have that much
- Regarding diet, it tries to make the best use of the nutrients given. Therefore, your muscles are fed primarily and your excessive body fat is being “burned”
Therefore, I believe that measuring your body weight works in most of the cases. The trick is that it shouldn’t affect your mood or confidence. You should know beforehand, that there might be great variability in body weight when you have consumed a high sodium meal or have not used the toilet for more than a day. So either hire a very good coach who can guide you through fat loss or get on that scale. I trust everyone who says, don’t measure your weight, check in with the mirror. That is what matters after all. But they forget one very important factor. Body recomposition is among the most difficult stuff to do. So numbers keep you on schedule. It can also be used as a wake-up call in case you find yourself indulging in sweets and treats.
Next part of the series is about the benefits of having less body fat, how to measure it and how to get rid of it.
If you any question regarding body fat and how is it created, let me know in the comments.

